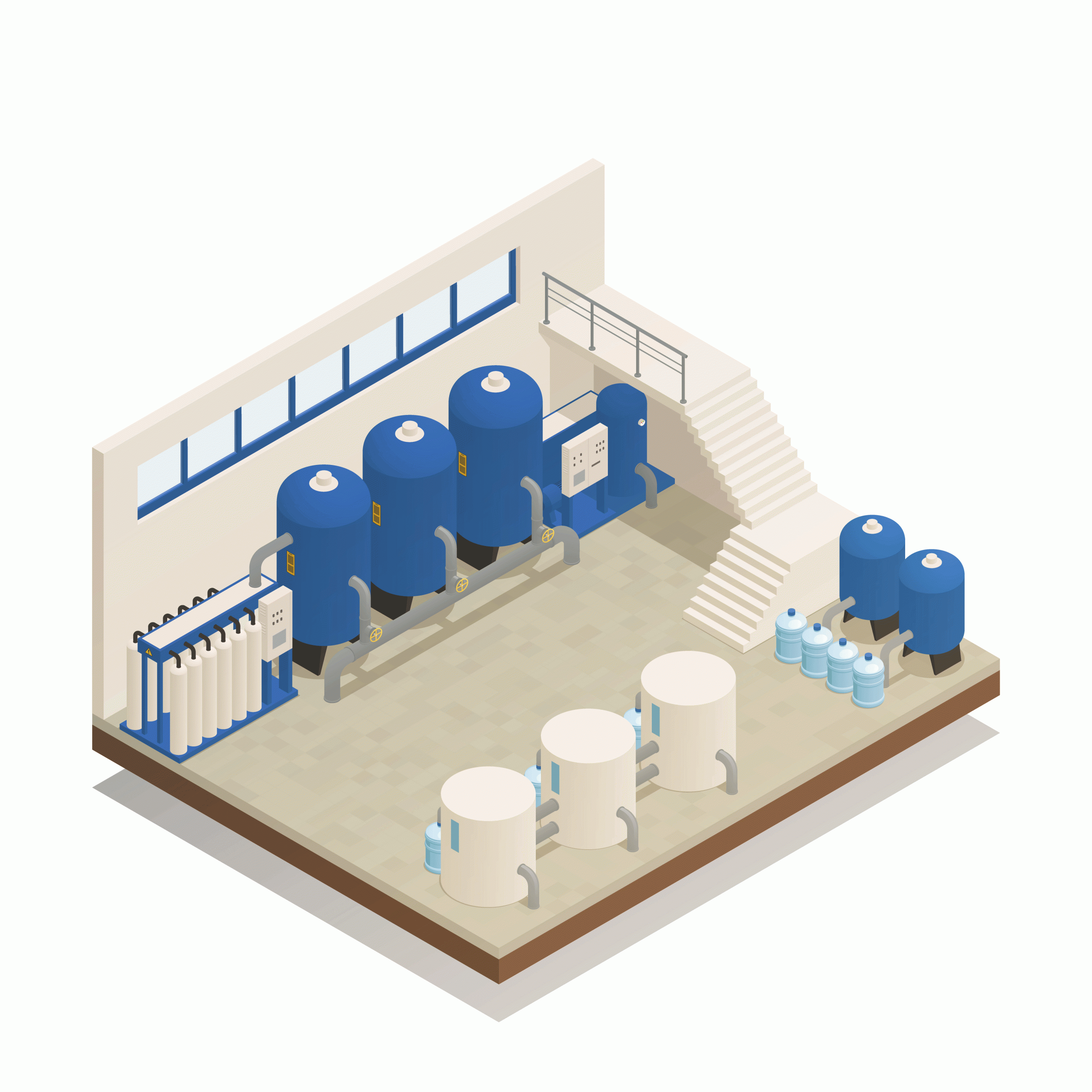
What is water treatment technology?
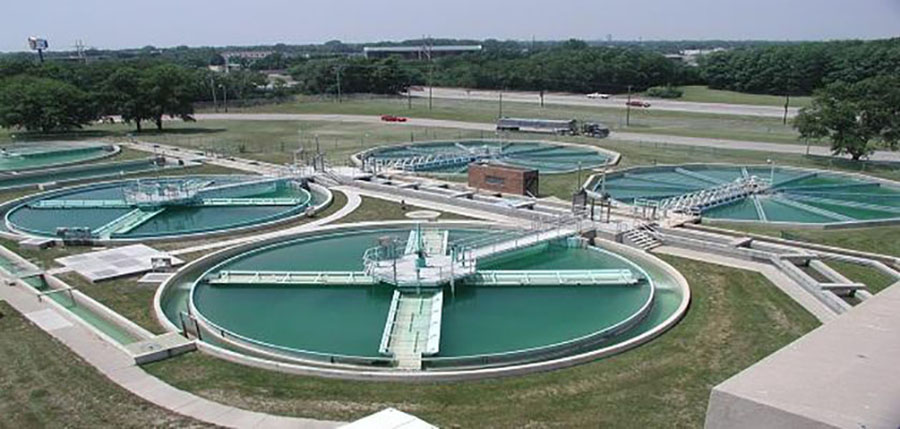
Water treatment technology, a term to describe the processes that are used to make water after treatment fit for a specific purpose. This includes its use as drinking water, as well as in industrial, medical, and other uses.
In general, the main purpose of water treatment is to remove or reduce any plankton or pollutants. So that the water is suitable for the purpose for which it is used.
The treatment processes differ according to the purpose of using the water, for example, drinking water focuses a lot on purifying the water from impurities, suspended matter, and resetting the number of mineral salts, or the total dissolved substances.
Drinking water treatment technology operations
The following processes represent a simplification of the drinking water treatment processes used globally:
- Pre-injection chlorine injection process to reduce algal blooms.
- Aeration with chlorine injection to break up the dissolved iron and manganese (by oxidation) and then remove them.
- Coagulation or coagulation to collect suspended matter.
- Sedimentation to separate solids or suspended matter.
- Filtration – to get rid of spilled material.
- Kill bacteria with antibiotics.
water treatment standards
Many developed countries set standards for their application within the country. In Europe for example, this includes the European Drinking Water Administration Directive 1988 and in the United States, the US Environmental Protection Agency sets standards as the Clean Drinking Water Act requires. For countries that do not have legislative or administrative frameworks for these standards, WHO publishes recommendations on standards to be achieved.
Industrial water treatment technology
Operations used
There are two basic industrial water treatment processes which are boiler water treatment and cooling water treatment. Correct water treatment in large quantities can cause solid components to react with bacteria in pipes and boiler houses. Steam boilers can tarnish, tarnish and corrode if left unattended. Limescale can seriously degrade machines, while additional fuel is required to heat the same amount of water due to increased thermal resistance. Dirty, poor-quality water can become a breeding ground for bacteria such as Legionella, which poses a public health risk.
Sometimes corrosion occurs in low-pressure boilers as a result of dissolved oxygen and hyperacidity or alkalinity. Thus the water treatment technology must remove the dissolved oxygen and keep the boiler water at an appropriate degree of acidity. Without effective water treatment, a water cooling system can suffer from scale formation, corrosion and contamination and become a breeding ground for harmful bacteria. This reduces efficiency, shortens reactor life, and makes operations inefficient and unsafe.
Boiler water treatment
Boiler water treatment is a type of industrial water treatment that focuses on removing or chemically modifying substances that can harm boilers. Different types of treatment are used in different locations in order to avoid limescale, corrosion, or mixing of steam with water mist (foaming). The external treatment of pure water sources for boiler use focuses on removing impurities before they reach the boiler. The internal treatment within the boiler focuses on reducing the solubility of water inside the boiler. As well as keeping the impurities in forms unable to cause damage before they can be removed from the boiler using high pressure blowing.
Cooling water treatment
Hydro cooling is a method of removing heat from industrial components and equipment. Water can be a more efficient heat transfer fluid when air cooling is ineffective. In some cases, water offers the advantage of heat transfer of a high specific temperature liquid in addition to evaporative cooling. Low cost often means that cooling water can be disposed of after a single use. Recycled cooling circuits can be pressurized to eliminate evaporation loss and provide greater flexibility and better hygiene.
Non-pressurized recirculating refrigeration circuits using evaporative cooling need continuous cleaning using high-pressure flow in order to remove accumulated impurities.
You can learn more about gray water treatment units here. And wastewater treatment from here.