Criteria for selecting the optimal chemical mixer for a water treatment plant
Selecting the optimal chemical mixer for water treatment plants is crucial for ensuring effective chemical dosing and achieving the required water quality. Chemical mixers, which blend, combine, or homogenize various materials, play a fundamental role in the treatment process, significantly impacting both operational efficiency and compliance with industry standards. Given the complex requirements of water treatment—including the need for precise chemical distribution and handling diverse chemical formulations—choosing the right mixer is essential for efficient treatment and minimizing environmental impact. Various types of mixers, such as motorized mixers, stationary mixers, ribbon mixers, and high-shear mixers, perform unique functions within water treatment processes.
Motorized mixers maintain material suspension under challenging mixing conditions, while stationary mixers offer an economical solution for continuous mixing by relying on fixed elements to enhance fluid turbulence. Ribbon mixers and high-shear mixers meet specific needs, such as blending dry powders or achieving fine particle dispersion, respectively. Each type of mixer has its own operational characteristics and requirements, which must be evaluated in light of the facility’s needs and the chemical properties being used. Key criteria for mixer selection include material compatibility, mixing capacity and efficiency, operational characteristics, durability, and compliance with industry regulations. These considerations directly impact not only the performance of the mixing process but also the overall safety and effectiveness of water treatment operations. Furthermore, cost considerations play a significant role, as the initial investment must be balanced against operating costs and long-term benefits, including energy efficiency and maintenance requirements.
Types of Chemical Mixers
Chemical mixers are specialized devices designed to mix, blend, and homogenize various materials. They play a crucial role in achieving homogeneity and consistency in chemical processes across various industries. In water treatment plants, selecting the appropriate type of mixer is critical to ensuring the effective dosing and mixing of chemicals, thereby improving overall treatment performance.
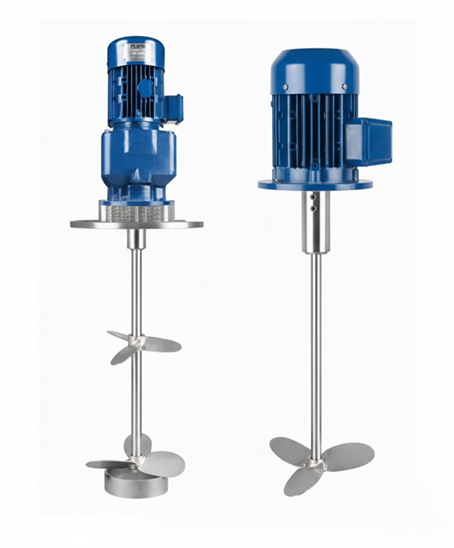
Agitators
Agitators are a common type of batch mixer, often referred to simply as mixers. They are particularly useful in situations where maintaining a chemical suspension is challenging. Agitators work by creating movement within the fluid, which helps to evenly distribute solid particles or enhance chemical reactions. Their versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from simple mixing tasks to more complex chemical reactions in water treatment processes.
Stationary Mixers
Stationary mixers are devices installed inside pipes that use fixed elements to create turbulence as fluids flow. Unlike conventional mixers, they do not require moving parts, making them easy to install and maintain. Stationary mixers are known for their cost-effectiveness, reducing chemical consumption and waste while providing consistent mixing results. They are particularly effective in continuous mixing processes in water treatment applications, where precise control of chemical dosages is critical.
This article covers all types of chemical mixers.
Mixing Mechanisms
Stationary mixers utilize various mechanisms, such as extension, folding, splitting, and shearing, to ensure efficient mixing of liquids and gases. The strategic arrangement of internal elements, such as baffles and channels, disrupts laminar flow, improving mixing efficiency. This design is essential for achieving chemical homogeneity, which is necessary to comply with treatment standards.
Key Selection Criteria
When selecting the optimal chemical mixer for a water treatment plant, several key criteria must be considered to ensure effective mixing, operational efficiency, and compliance with industry standards.
Compatibility with Materials
The mixer’s compatibility with the chemicals and materials being processed is crucial. Different mixers are designed to handle specific material properties such as viscosity, density, and chemical reactivity. For example, emulsifiers are used to create stable emulsions by combining immiscible liquids, while laboratory mixers focus on small-scale, precise tasks required for research and development. Ensuring the selected mixer can accommodate the specific materials being processed significantly impacts the quality of the mixing process.
Mixing Capacity and Efficiency
It is essential to select a mixer that is appropriate for the required batch size or production range. The mixing capacity should be suitable for the operational requirements of the water treatment plant. Furthermore, mixing efficiency, defined as the ratio of the effectiveness of the mixing process to the time or energy required, is a primary consideration. High-speed mixers, such as vertically agitated mixers, may be necessary for mixing materials with varying viscosities. While slower mixers may be more suitable for applications requiring gentle agitation.
Operational Features and Customization
Evaluating the operational features of a mixer is crucial for achieving optimal performance. Factors such as speed, programmability, and advanced functions (like variable frequency drives for improved speed control) can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the mixing process. Additionally, mixers offering customization options can be designed to meet the specific needs of a water treatment plant.
Durability and Maintenance
The durability of the mixer materials plays a significant role in long-term performance. Robust construction and corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel, can minimize wear and tear, thus reducing maintenance requirements. A comprehensive understanding of expected maintenance intervals and the lifespan of consumable parts is essential for Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
Compliance with Industry Standards
In sectors such as water treatment, compliance with relevant industry standards and regulations is crucial. It ensures that mixing equipment is safe, fit for purpose, and meets audit or regulatory requirements. Manufacturers committed to these standards can provide mixers that not only perform efficiently but also meet essential safety and hygiene requirements in treatment processes.
Cost Considerations
While initial cost is often a major concern, it is important to consider the total cost of ownership. That includes the long-term value derived from energy efficiency, maintenance, and operational reliability. A slightly higher initial investment in a high-performance mixer can lead to improved consistency, reduced downtime, and fewer process disruptions, resulting in a positive return on investment. By carefully evaluating these criteria, water treatment plants can make informed decisions when selecting chemical mixers. That will enhance their operational efficiency and ensure effective treatment outcomes.
Factors Influencing Selection
Selecting the optimal chemical mixer for a water treatment plant requires a comprehensive evaluation of several critical factors. These factors ensure that the chosen mixer effectively meets the specific requirements of the treatment processes while maintaining safety and efficiency.
Medium Characteristics
Understanding the characteristics of the medium to be mixed is crucial. Factors such as the type of chemicals used—whether dry, liquid, or gaseous—significantly influence mixer selection. For example, common chemicals include sodium bicarbonate, aluminum sulfate, and chlorine. Each requires different mixing strategies and equipment designs to ensure effective dosing and mixing.
Chemical Compatibility and Material Selection
The chemical compatibility of the mixer material with the materials being treated is essential to prevent damage and ensure longevity. Materials such as stainless steel, Teflon, and specialized plastics are often preferred for their resistance to corrosion and chemical attack. Additionally, protective liners may be necessary to protect against harsh chemicals.
Mixing Capacity and Flow Dynamics
The mixing capacity must be appropriate for the required production volume and batch size for the application. The flow rate and pipeline velocity must be evaluated. In addition to the flow rate of injected chemicals, the mixing process is optimized to maintain system efficiency.
Ensuring compliance with safety regulations and proper handling of hazardous materials. The use of safety devices such as safety valves and secondary containment systems are crucial for protecting both personnel and the environment. By carefully analyzing these factors, water treatment plants can select a mixer that improves operational efficiency, ensures compliance, and ultimately contributes to better public health and environmental outcomes.